What Is 12x3 9x2 4x 3 In Factored Form
planetorganic
Nov 30, 2025 · 7 min read
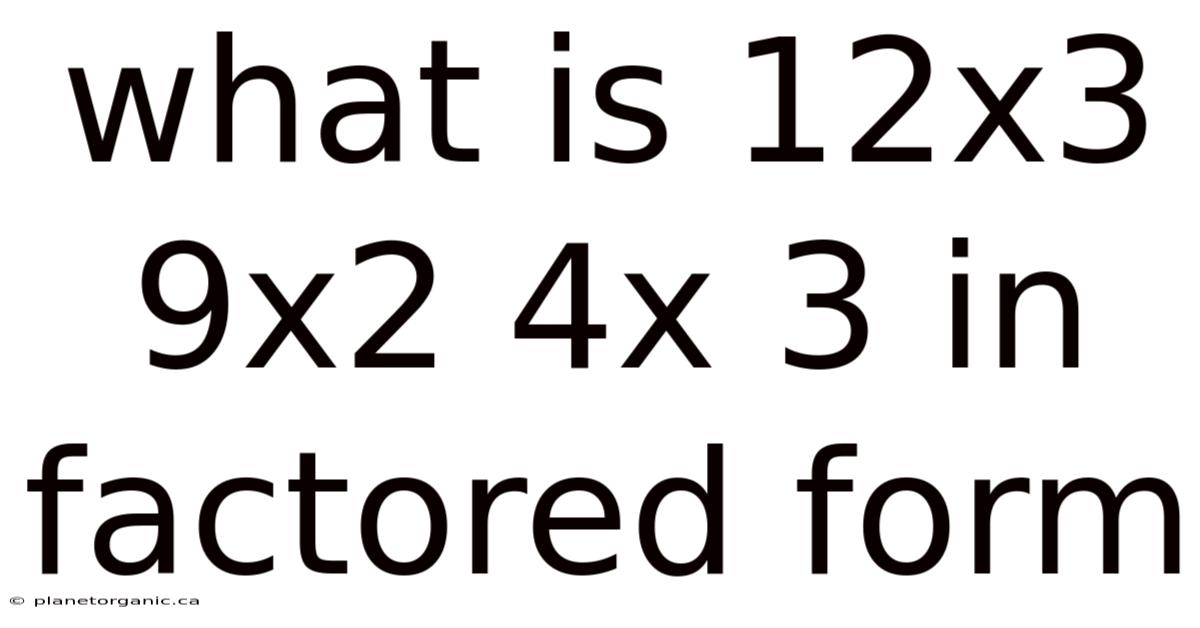
Table of Contents
Understanding Factored Form: Breaking Down 12x³ + 9x² + 4x
The journey into the world of algebra often leads us to expressions that seem complex at first glance. One such expression is 12x³ + 9x² + 4x. To truly understand and simplify this expression, we turn to the concept of factored form. Factoring, in essence, is the process of breaking down an expression into smaller, more manageable components. This not only simplifies the expression but also reveals underlying relationships and patterns that might not be immediately obvious.
In this detailed exploration, we'll delve into the step-by-step process of factoring the expression 12x³ + 9x² + 4x. We'll unravel the underlying principles, demystify the techniques, and provide a clear, accessible pathway for anyone looking to master this fundamental algebraic skill.
Why Factoring Matters: More Than Just Simplification
Before we dive into the specifics, let's take a moment to appreciate why factoring is such a crucial concept in mathematics. Factoring is not just a mere exercise in simplification; it is a gateway to solving equations, understanding functions, and tackling more advanced mathematical concepts.
-
Solving Equations: Factoring allows us to find the roots or solutions of polynomial equations. By setting a factored expression equal to zero, we can easily identify the values of the variable that make the equation true.
-
Simplifying Expressions: Factoring can significantly reduce the complexity of algebraic expressions, making them easier to work with and understand.
-
Identifying Patterns: Factoring can reveal hidden patterns and relationships within mathematical expressions, leading to deeper insights and a more intuitive understanding.
-
Advanced Mathematics: Factoring is a fundamental skill that forms the basis for many advanced mathematical concepts, including calculus, linear algebra, and differential equations.
Step-by-Step Guide: Factoring 12x³ + 9x² + 4x
Now, let's get to the heart of the matter: factoring the expression 12x³ + 9x² + 4x. We'll break down the process into clear, manageable steps, providing explanations and examples along the way.
Step 1: Identifying the Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
The first and most crucial step in factoring any expression is to identify the greatest common factor (GCF) of all the terms. The GCF is the largest factor that divides evenly into each term in the expression. In our case, the expression is 12x³ + 9x² + 4x.
-
Analyzing the Coefficients: The coefficients are 12, 9, and 4. The greatest common factor of these numbers is 1, as they share no common factors other than 1.
-
Analyzing the Variables: The variables are x³, x², and x. The greatest common factor of these terms is x, as it is the lowest power of x present in all the terms.
Therefore, the greatest common factor (GCF) of the entire expression 12x³ + 9x² + 4x is x.
Step 2: Factoring Out the GCF
Now that we've identified the GCF, we can factor it out of the expression. This involves dividing each term in the expression by the GCF and writing the GCF outside of the parentheses.
12x³ + 9x² + 4x = x(12x² + 9x + 4)
We have successfully factored out the GCF, x, from the original expression. The resulting expression inside the parentheses is 12x² + 9x + 4.
Step 3: Analyzing the Remaining Quadratic Expression
After factoring out the GCF, we are left with a quadratic expression inside the parentheses: 12x² + 9x + 4. To determine if this quadratic expression can be factored further, we need to analyze it closely.
-
Checking for Simple Factoring: We can attempt to factor the quadratic expression using simple factoring techniques, such as finding two numbers that multiply to the constant term (4) and add up to the coefficient of the linear term (9). However, in this case, it is unlikely that we will find such numbers.
-
Using the Discriminant: A more reliable way to determine if a quadratic expression can be factored is to use the discriminant. The discriminant is a value that is calculated from the coefficients of the quadratic expression and can tell us about the nature of the roots.
The discriminant (D) is calculated using the following formula:
D = b² - 4ac
where a, b, and c are the coefficients of the quadratic expression ax² + bx + c.
In our case, a = 12, b = 9, and c = 4. Plugging these values into the formula, we get:
D = 9² - 4 * 12 * 4 = 81 - 192 = -111
Since the discriminant is negative, the quadratic expression 12x² + 9x + 4 has no real roots. This means that it cannot be factored further using real numbers.
Step 4: Final Factored Form
Based on our analysis, the quadratic expression 12x² + 9x + 4 cannot be factored further. Therefore, the final factored form of the original expression 12x³ + 9x² + 4x is:
x(12x² + 9x + 4)
This is the simplest form of the expression that can be achieved through factoring.
Alternative Approaches to Factoring
While we have successfully factored the expression 12x³ + 9x² + 4x, it's worth exploring alternative approaches to factoring, as they can be useful in different scenarios.
-
Factoring by Grouping: This technique involves grouping terms in the expression and factoring out common factors from each group. However, this method is not applicable to our expression, as it does not have enough terms to form meaningful groups.
-
Using the Quadratic Formula: The quadratic formula can be used to find the roots of a quadratic expression, even if it cannot be factored easily. However, in our case, the discriminant is negative, which means that the roots are complex numbers. While we could express the factored form using complex numbers, it is generally not necessary or desirable unless specifically requested.
-
Numerical Methods: In cases where analytical factoring is not possible, numerical methods can be used to approximate the roots of the expression. These methods involve using iterative algorithms to find values of x that make the expression close to zero.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Factoring can be tricky, and it's easy to make mistakes along the way. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
-
Forgetting to Factor Out the GCF: Always start by looking for the greatest common factor. Failing to do so can make the factoring process much more difficult.
-
Incorrectly Identifying the GCF: Make sure you accurately identify the largest factor that divides evenly into all the terms.
-
Making Arithmetic Errors: Pay close attention to your arithmetic when dividing terms by the GCF and when calculating the discriminant.
-
Assuming All Quadratic Expressions Can Be Factored: Not all quadratic expressions can be factored using real numbers. Use the discriminant to determine if factoring is possible.
-
Stopping Too Early: Ensure that you have factored the expression completely before stopping. Check if the resulting expression can be factored further.
Real-World Applications of Factoring
Factoring is not just an abstract mathematical concept; it has numerous real-world applications in various fields, including:
-
Engineering: Factoring is used in structural engineering to analyze the stability of buildings and bridges.
-
Physics: Factoring is used in physics to solve equations related to motion, energy, and momentum.
-
Computer Science: Factoring is used in computer science to optimize algorithms and data structures.
-
Economics: Factoring is used in economics to model economic growth and predict market trends.
-
Finance: Factoring is used in finance to calculate investment returns and assess risk.
Expanding Your Knowledge: Further Exploration
If you're interested in learning more about factoring, here are some resources that you might find helpful:
-
Textbooks: Consult algebra textbooks for detailed explanations and examples of factoring techniques.
-
Online Tutorials: Websites like Khan Academy and Coursera offer free tutorials and videos on factoring.
-
Practice Problems: Work through practice problems to solidify your understanding of factoring.
-
Math Forums: Join online math forums to ask questions and discuss factoring with other learners.
The Beauty of Factoring: A Deeper Appreciation
Factoring, at its core, is about understanding the structure and relationships within mathematical expressions. It's about breaking down complex problems into simpler, more manageable components. It's about revealing hidden patterns and insights that might not be immediately obvious.
As you delve deeper into the world of mathematics, you'll discover that factoring is not just a skill; it's a way of thinking. It's a way of approaching problems with a sense of curiosity, creativity, and a desire to understand the underlying principles.
In Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Factoring
We've journeyed through the process of factoring the expression 12x³ + 9x² + 4x, step by step. We've explored the underlying principles, demystified the techniques, and highlighted the importance of factoring in mathematics and beyond.
Remember, factoring is a skill that takes practice and patience to master. Don't be discouraged if you encounter challenges along the way. Keep practicing, keep exploring, and keep asking questions. With dedication and perseverance, you'll unlock the power of factoring and gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and elegance of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 12x3 9x2 4x 3 In Factored Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.