How Many Grams Are In 88.1 Moles Of Magnesium
planetorganic
Nov 12, 2025 · 10 min read
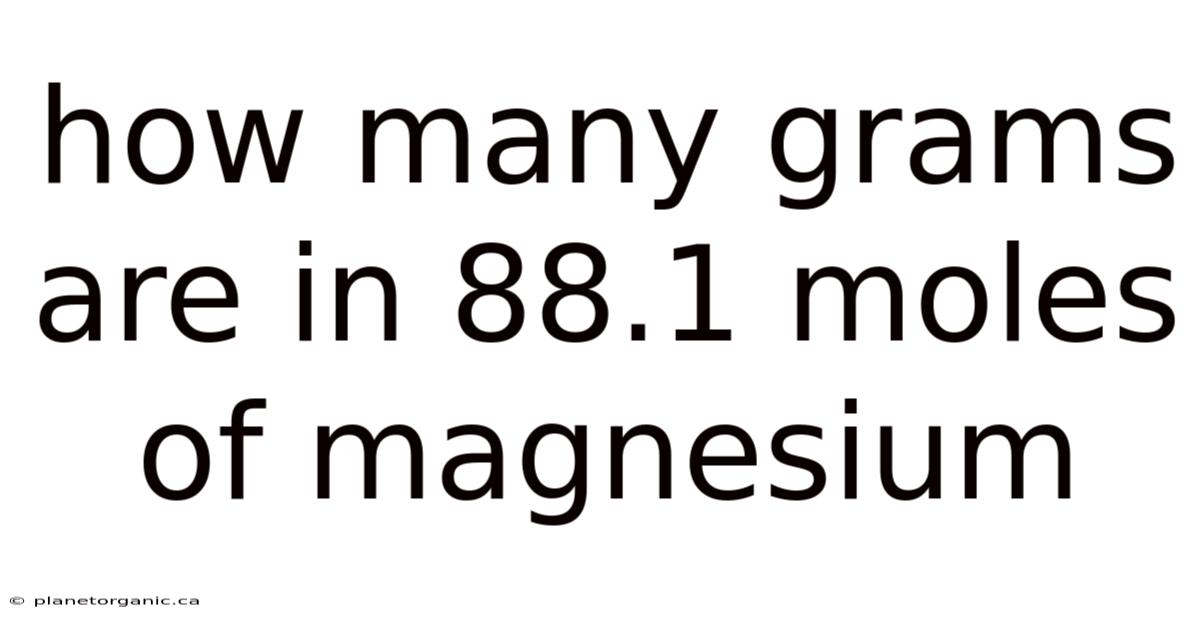
Table of Contents
Unlocking the secrets of chemical calculations often involves understanding the relationship between moles and grams, a fundamental concept in chemistry. In this exploration, we will delve into how to convert moles of magnesium into grams, specifically focusing on 88.1 moles of magnesium (Mg). This conversion is crucial in various applications, from laboratory experiments to industrial processes, where accurate measurements are essential for achieving desired outcomes.
Understanding Moles and Grams
Before diving into the calculation, it's essential to understand the concepts of moles and grams and their significance in chemistry.
-
Mole: A mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance. It is defined as the amount of any substance that contains as many constituent particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. This number is known as Avogadro's number, approximately 6.022 x 10^23.
-
Gram: A gram is a unit of mass in the metric system. It is commonly used in chemistry to measure the mass of substances in laboratory settings.
The relationship between moles and grams is established through the molar mass of a substance, which is the mass of one mole of that substance. The molar mass is numerically equivalent to the atomic or molecular weight of the substance in atomic mass units (amu), but expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Determining the Molar Mass of Magnesium
To convert moles of magnesium to grams, we need to know the molar mass of magnesium (Mg). The molar mass of an element can be found on the periodic table.
- Locate magnesium (Mg) on the periodic table.
- Find the atomic mass of magnesium. The atomic mass of magnesium is approximately 24.305 amu.
- Convert the atomic mass to molar mass by expressing it in grams per mole (g/mol). Therefore, the molar mass of magnesium is 24.305 g/mol.
Conversion Formula
The formula to convert moles to grams is:
Mass (grams) = Number of Moles × Molar Mass
This formula allows us to easily convert from moles to grams by multiplying the number of moles by the molar mass of the substance.
Step-by-Step Calculation: Converting 88.1 Moles of Magnesium to Grams
Now that we know the molar mass of magnesium and the conversion formula, we can calculate the mass of 88.1 moles of magnesium.
-
Identify the given values:
- Number of moles of magnesium = 88.1 moles
- Molar mass of magnesium = 24.305 g/mol
-
Apply the conversion formula:
- Mass (grams) = Number of Moles × Molar Mass
- Mass (grams) = 88.1 moles × 24.305 g/mol
-
Perform the calculation:
- Mass (grams) = 2141.2705 grams
Therefore, 88.1 moles of magnesium is equal to approximately 2141.2705 grams.
Practical Applications
Understanding how to convert moles to grams is crucial in various practical applications in chemistry and related fields.
-
Laboratory Experiments: In chemical reactions, precise amounts of reactants are required to achieve desired products. Converting moles to grams allows chemists to accurately weigh out substances needed for experiments.
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes involve chemical reactions that require specific quantities of reactants. Converting moles to grams ensures that the correct amounts of substances are used, optimizing reaction efficiency and product yield.
-
Stoichiometry: Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. Converting moles to grams is essential for stoichiometric calculations, allowing chemists to predict the amount of product formed from a given amount of reactant.
-
Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, precise measurements of chemicals are critical for drug development and manufacturing. Converting moles to grams ensures that the correct amounts of active ingredients and excipients are used in drug formulations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When converting moles to grams, it's essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate results.
-
Using the Wrong Molar Mass: Always ensure that you are using the correct molar mass for the substance you are converting. Double-check the periodic table or reliable sources to confirm the molar mass of the element or compound.
-
Incorrectly Applying the Conversion Formula: Make sure to apply the conversion formula correctly. Multiply the number of moles by the molar mass to get the mass in grams.
-
Rounding Errors: Be mindful of rounding errors, especially in multi-step calculations. Retain as many significant figures as possible throughout the calculation and round the final answer to the appropriate number of significant figures.
-
Unit Conversion Errors: Ensure that you are using consistent units throughout the calculation. If the molar mass is in grams per mole (g/mol), the number of moles should be in moles (mol) to obtain the mass in grams (g).
Additional Examples
To further illustrate the conversion of moles to grams, let's consider a few more examples:
Example 1: Converting 2.5 moles of Sodium Chloride (NaCl) to Grams
-
Determine the molar mass of NaCl:
- Molar mass of Na = 22.99 g/mol
- Molar mass of Cl = 35.45 g/mol
- Molar mass of NaCl = 22.99 g/mol + 35.45 g/mol = 58.44 g/mol
-
Apply the conversion formula:
- Mass (grams) = Number of Moles × Molar Mass
- Mass (grams) = 2.5 moles × 58.44 g/mol
-
Perform the calculation:
- Mass (grams) = 146.1 grams
Therefore, 2.5 moles of sodium chloride is equal to 146.1 grams.
Example 2: Converting 0.75 moles of Water (H2O) to Grams
-
Determine the molar mass of H2O:
- Molar mass of H = 1.008 g/mol
- Molar mass of O = 16.00 g/mol
- Molar mass of H2O = (2 × 1.008 g/mol) + 16.00 g/mol = 18.016 g/mol
-
Apply the conversion formula:
- Mass (grams) = Number of Moles × Molar Mass
- Mass (grams) = 0.75 moles × 18.016 g/mol
-
Perform the calculation:
- Mass (grams) = 13.512 grams
Therefore, 0.75 moles of water is equal to 13.512 grams.
Advanced Concepts
Delving deeper into the concept of moles and grams, it's essential to understand related advanced concepts that build upon this fundamental knowledge.
-
Molarity: Molarity is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution. It is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution (mol/L). Understanding molarity allows chemists to prepare solutions of specific concentrations for experiments and reactions.
-
Molality: Molality is another measure of concentration, defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent (mol/kg). Unlike molarity, molality is independent of temperature, making it useful in situations where temperature variations may affect the volume of the solution.
-
Empirical and Molecular Formulas: The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound, while the molecular formula represents the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule. Converting grams to moles and vice versa is crucial in determining both empirical and molecular formulas.
-
Limiting Reactant: In chemical reactions, the limiting reactant is the reactant that is completely consumed first, determining the maximum amount of product that can be formed. Converting grams to moles helps identify the limiting reactant and calculate the theoretical yield of the reaction.
The Role of Significant Figures
When performing calculations in chemistry, it's important to pay attention to significant figures to ensure the accuracy and precision of the results.
-
Definition: Significant figures are the digits in a number that are known with certainty plus one uncertain digit. They indicate the precision of a measurement or calculation.
-
Rules for Significant Figures:
- All non-zero digits are significant.
- Zeros between non-zero digits are significant.
- Leading zeros are not significant.
- Trailing zeros in a number containing a decimal point are significant.
-
Significant Figures in Calculations:
- When multiplying or dividing, the result should have the same number of significant figures as the number with the fewest significant figures.
- When adding or subtracting, the result should have the same number of decimal places as the number with the fewest decimal places.
In the conversion of 88.1 moles of magnesium to grams, the number 88.1 has three significant figures, and the molar mass of magnesium (24.305 g/mol) has five significant figures. Therefore, the final answer should be rounded to three significant figures:
Mass (grams) = 88.1 moles × 24.305 g/mol ≈ 2140 grams
Importance of Unit Analysis
Unit analysis, also known as dimensional analysis, is a problem-solving method that uses the units of measurement to guide calculations. It is a powerful tool for checking the validity of calculations and ensuring that the final answer has the correct units.
- How Unit Analysis Works:
- Write down the given quantity with its units.
- Multiply by conversion factors to cancel unwanted units and obtain the desired units.
- Ensure that the units cancel out correctly.
In the conversion of moles to grams, unit analysis can be used to verify that the final answer is in grams:
- 1 moles Mg × (24.305 grams Mg / 1 mole Mg) = 2141.2705 grams Mg
The moles Mg unit cancels out, leaving the answer in grams Mg, which is the desired unit.
Real-World Examples
The conversion of moles to grams is not just a theoretical exercise; it has numerous real-world applications across various industries and fields.
-
Environmental Science: In environmental monitoring, chemists often need to determine the concentration of pollutants in soil, water, or air samples. Converting moles to grams allows them to express these concentrations in more practical units, such as milligrams per liter (mg/L) or parts per million (ppm).
-
Materials Science: Materials scientists use moles and grams to characterize the composition of materials and to design new materials with specific properties. Converting moles to grams helps them calculate the amounts of different elements or compounds needed to create a material with a desired stoichiometry.
-
Agriculture: In agriculture, understanding the mole-to-gram conversion is crucial for calculating the amount of fertilizers needed to provide plants with essential nutrients. Farmers and agricultural scientists use this conversion to determine the correct amount of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium required for optimal plant growth.
-
Food Science: Food scientists use moles and grams to analyze the nutritional content of food products and to develop new food formulations. Converting moles to grams helps them determine the amount of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in a food sample, as well as the amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Historical Context
The concept of the mole has evolved over time, with contributions from numerous scientists and researchers.
-
Early Concepts: The idea of a fixed number of particles in a given amount of substance dates back to the work of Amedeo Avogadro in the early 19th century. Avogadro proposed that equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules.
-
Development of the Mole Concept: The term "mole" was first used by Wilhelm Ostwald in 1896 to describe the amount of a substance containing a specific number of molecules. However, it was not until the 20th century that the mole became a standardized unit of measurement in chemistry.
-
Standardization of Avogadro's Number: The value of Avogadro's number, which defines the number of particles in a mole, has been refined over the years through experimental measurements. Today, Avogadro's number is defined as 6.02214076 × 10^23 particles per mole.
Conclusion
Converting moles to grams is a fundamental skill in chemistry with wide-ranging applications in laboratory experiments, industrial processes, and various scientific disciplines. By understanding the relationship between moles and grams, chemists can accurately measure and manipulate substances to achieve desired outcomes. In this exploration, we've demonstrated how to convert 88.1 moles of magnesium to grams, highlighting the importance of molar mass, conversion formulas, and unit analysis. Furthermore, we've delved into advanced concepts and real-world examples to provide a comprehensive understanding of this essential concept. Mastering the conversion of moles to grams is a crucial step in building a strong foundation in chemistry and related fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Consider The Following Graph Of An Absolute Value Function
Nov 12, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Guideline For Establishing Causality
Nov 12, 2025
-
Find The Population Mean Or Sample Mean As Indicated
Nov 12, 2025
-
Ap Biology Phylogeny Review Worksheet Answers
Nov 12, 2025
-
Unit 2 Progress Check Mcq Part A Ap Gov
Nov 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Grams Are In 88.1 Moles Of Magnesium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.