2 X 3 4 X 1
planetorganic
Nov 02, 2025 · 8 min read
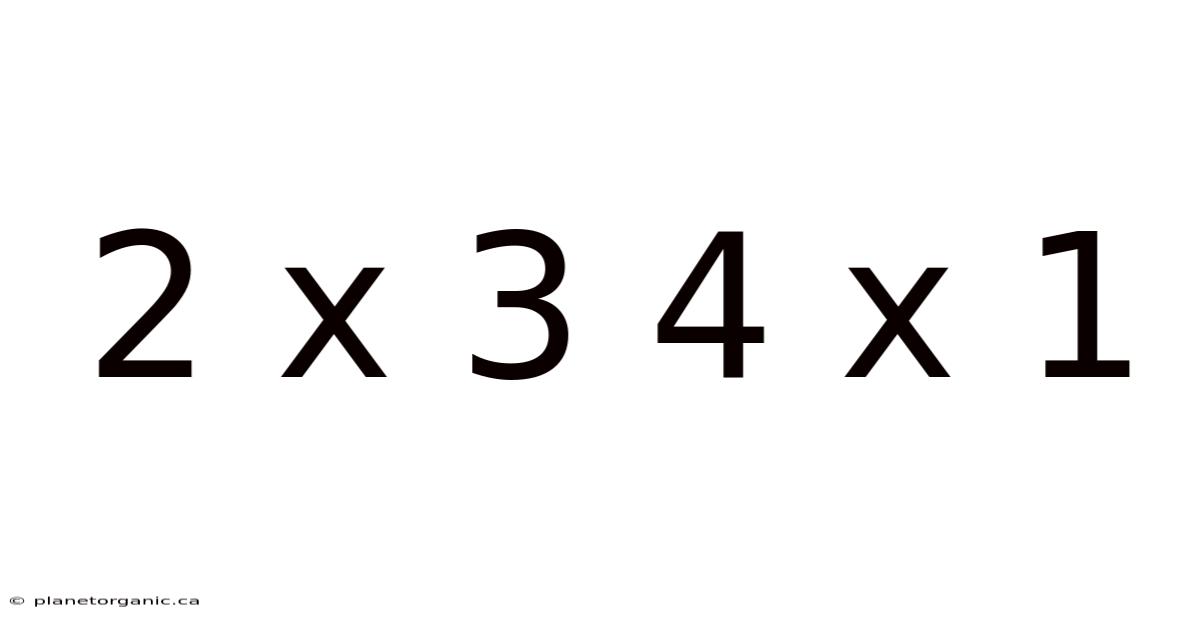
Table of Contents
The world of mathematics often presents seemingly simple expressions that, upon closer inspection, reveal layers of complexity and multiple valid interpretations. The expression "2 x 3 4 x 1" is a prime example of this, sparking debate and highlighting the importance of order of operations and mathematical conventions. This exploration will delve into the different ways to interpret this expression, examining the mathematical principles that underpin each interpretation, and providing a comprehensive understanding of how to arrive at the correct answer.
Interpreting "2 x 3 4 x 1": A Matter of Perspective
The expression "2 x 3 4 x 1" is inherently ambiguous because it lacks explicit grouping symbols such as parentheses or brackets. This ambiguity leads to different possible interpretations depending on the order in which the operations are performed. The two primary interpretations revolve around whether the multiplication and implied addition are performed from left to right or whether there is an implied grouping.
Interpretation 1: Left-to-Right Evaluation
This interpretation follows the basic convention of performing operations from left to right when no other rules dictate otherwise. In this case, the expression is evaluated as follows:
- 2 x 3 = 6
- 6 4 = 10
- 10 x 1 = 10
Therefore, according to the left-to-right evaluation, the answer is 10.
Interpretation 2: Implied Addition and Multiplication
This interpretation assumes that "3 4" is a single number obtained by adding 3 and 4. This could be due to the way the expression is written or a prior understanding of the context. If this assumption is made, the expression is evaluated as follows:
- 3 4 = 7
- 2 x 7 = 14
- 14 x 1 = 14
Therefore, according to this interpretation, the answer is 14.
The Importance of Order of Operations: PEMDAS/BODMAS
To avoid ambiguity and ensure consistent results, mathematicians have established a standard order of operations, often remembered by the acronyms PEMDAS or BODMAS:
- PEMDAS: Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (from left to right), Addition and Subtraction (from left to right).
- BODMAS: Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication (from left to right), Addition and Subtraction (from left to right).
Both acronyms represent the same hierarchy of operations. Applying PEMDAS/BODMAS to the expression "2 x 3 4 x 1" clarifies the intended order.
Applying PEMDAS/BODMAS to "2 x 3 4 x 1"
The presence of both multiplication and addition in the expression necessitates the application of PEMDAS/BODMAS. According to the order of operations, multiplication should be performed before addition. Therefore, the expression needs to be rearranged or interpreted in a way that respects this rule.
To properly apply PEMDAS/BODMAS, we must understand that "3 4" without any connecting operator is not a standard mathematical notation. It's more likely a typographical error or an intentional ambiguity. To resolve this, we need to consider different possibilities.
Scenario 1: Assuming a Missing Operator
If we assume there's a missing operator between "3" and "4", the most likely candidate is either addition (+) or multiplication (x). Let's analyze both scenarios:
-
If the missing operator is addition (+): The expression becomes 2 x 3 + 4 x 1. Applying PEMDAS/BODMAS, we get:
- 2 x 3 = 6
- 4 x 1 = 4
- 6 + 4 = 10
Therefore, the answer is 10.
-
If the missing operator is multiplication (x): The expression becomes 2 x 3 x 4 x 1. Applying PEMDAS/BODMAS, we get:
- 2 x 3 = 6
- 6 x 4 = 24
- 24 x 1 = 24
Therefore, the answer is 24.
Scenario 2: Assuming "3 4" Represents a Single Number (Concatenation)
In some contexts, especially in computer science or specific mathematical notations, "3 4" might be interpreted as the concatenation of the digits 3 and 4, forming the number 34. In this case, the expression becomes 2 x 34 x 1. Applying PEMDAS/BODMAS, we get:
- 2 x 34 = 68
- 68 x 1 = 68
Therefore, the answer is 68. This interpretation is less common in standard mathematical notation but plausible depending on the context.
Scenario 3: Intended as (2 x 3) (4 x 1)
It's possible the expression was intended to represent the product of two separate expressions, (2 x 3) and (4 x 1), with the space between them representing multiplication. In this case:
- 2 x 3 = 6
- 4 x 1 = 4
- 6 x 4 = 24
Therefore, the answer is 24.
The Role of Context and Intended Meaning
The correct interpretation of "2 x 3 4 x 1" hinges on the context in which it is presented and the intended meaning behind it. Without explicit grouping symbols or a clear indication of the intended operations, the expression remains ambiguous.
-
Mathematical Textbooks: In a standard mathematical textbook, the most likely interpretation, assuming a missing operator, is 2 x 3 + 4 x 1 = 10, due to the application of PEMDAS/BODMAS.
-
Programming: In a programming context, if the intention is to concatenate, 2 x 34 x 1 = 68 might be valid.
-
Casual Usage: In casual usage, the intended meaning could vary, making it crucial to seek clarification.
Resolving Ambiguity: The Power of Parentheses
The ambiguity surrounding "2 x 3 4 x 1" highlights the importance of using parentheses or brackets to clearly define the intended order of operations. By adding these grouping symbols, the expression becomes unambiguous and leaves no room for misinterpretation. Here are a few examples:
-
(2 x 3) + (4 x 1): This clearly indicates that 2 is multiplied by 3, 4 is multiplied by 1, and then the two results are added. The answer is 6 + 4 = 10.
-
2 x (3 + 4) x 1: This indicates that 3 and 4 are added first, and then the result is multiplied by 2 and 1. The answer is 2 x 7 x 1 = 14.
-
2 x (3 x 4) x 1: This indicates that 3 and 4 are multiplied first, and then the result is multiplied by 2 and 1. The answer is 2 x 12 x 1 = 24.
-
(2 x 3 4) x 1: This is still ambiguous because "2 x 3 4" lacks a defined operation between 3 and 4.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Several common mistakes can lead to incorrect interpretations of expressions like "2 x 3 4 x 1":
- Ignoring the Order of Operations: Failing to adhere to PEMDAS/BODMAS is a primary source of error.
- Assuming Left-to-Right Evaluation Always: While left-to-right evaluation is a general guideline, it's superseded by the order of operations.
- Overlooking Implied Operations: Sometimes, mathematical expressions imply operations that are not explicitly written, such as multiplication by juxtaposition (e.g., 2(3+4)).
- Misinterpreting Concatenation: Confusing concatenation (joining digits) with standard arithmetic operations.
- Failing to Recognize Ambiguity: Not acknowledging the inherent ambiguity in an expression lacking clear grouping symbols.
Practical Implications and Real-World Examples
Understanding the order of operations and the potential for ambiguity in mathematical expressions is crucial in various fields:
- Computer Programming: Programming languages rely heavily on precise syntax and the correct interpretation of mathematical expressions. Incorrect order of operations can lead to bugs and unexpected program behavior.
- Spreadsheet Software: Spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets use formulas that involve mathematical operations. Understanding the order of operations is essential for creating accurate and reliable calculations.
- Engineering and Science: Engineers and scientists regularly use mathematical equations and models to solve complex problems. Accurate calculations are critical for ensuring the safety and reliability of designs and experiments.
- Finance: Financial calculations, such as calculating interest rates or investment returns, require a thorough understanding of mathematical principles and the order of operations.
- Everyday Life: Even in everyday situations, such as calculating discounts or splitting bills, a basic understanding of mathematical operations is helpful for avoiding errors.
Advanced Considerations: Operator Precedence and Associativity
While PEMDAS/BODMAS provides a general framework, more advanced mathematical contexts introduce concepts like operator precedence and associativity.
- Operator Precedence: Different operators have different levels of precedence. For example, exponentiation typically has higher precedence than multiplication.
- Associativity: When operators of the same precedence appear in an expression, associativity determines the order in which they are evaluated. For example, subtraction is left-associative (a - b - c is evaluated as (a - b) - c), while exponentiation is right-associative (a ^ b ^ c is evaluated as a ^ (b ^ c)).
Understanding these concepts is crucial for working with more complex mathematical expressions and programming languages.
Conclusion: Clarity and Precision in Mathematics
The expression "2 x 3 4 x 1" serves as a valuable lesson in the importance of clarity and precision in mathematics. While the expression itself is simple, its ambiguity highlights the need for:
- Understanding the Order of Operations: PEMDAS/BODMAS provides a standard framework for evaluating mathematical expressions.
- Using Grouping Symbols: Parentheses and brackets eliminate ambiguity and clearly define the intended order of operations.
- Considering Context: The intended meaning of an expression can vary depending on the context in which it is presented.
- Communicating Clearly: When writing or interpreting mathematical expressions, it's crucial to communicate clearly and avoid ambiguity.
By adhering to these principles, we can ensure accurate calculations and avoid misunderstandings in mathematics and related fields. The seemingly simple expression "2 x 3 4 x 1" underscores the fact that even the most basic mathematical concepts require careful attention and a commitment to precision. Ultimately, the most responsible approach is to always seek clarification or add parentheses to ensure the intended calculation is performed, leading to the correct and unambiguous result. Whether the intended meaning is 10, 14, 24, or even 68, the key is understanding why each answer is possible and how to eliminate the ambiguity in the first place.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 X 3 4 X 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.